Projects
Research Projects
🧬 Morpho-VAE: Morphological Difference Representation Learning
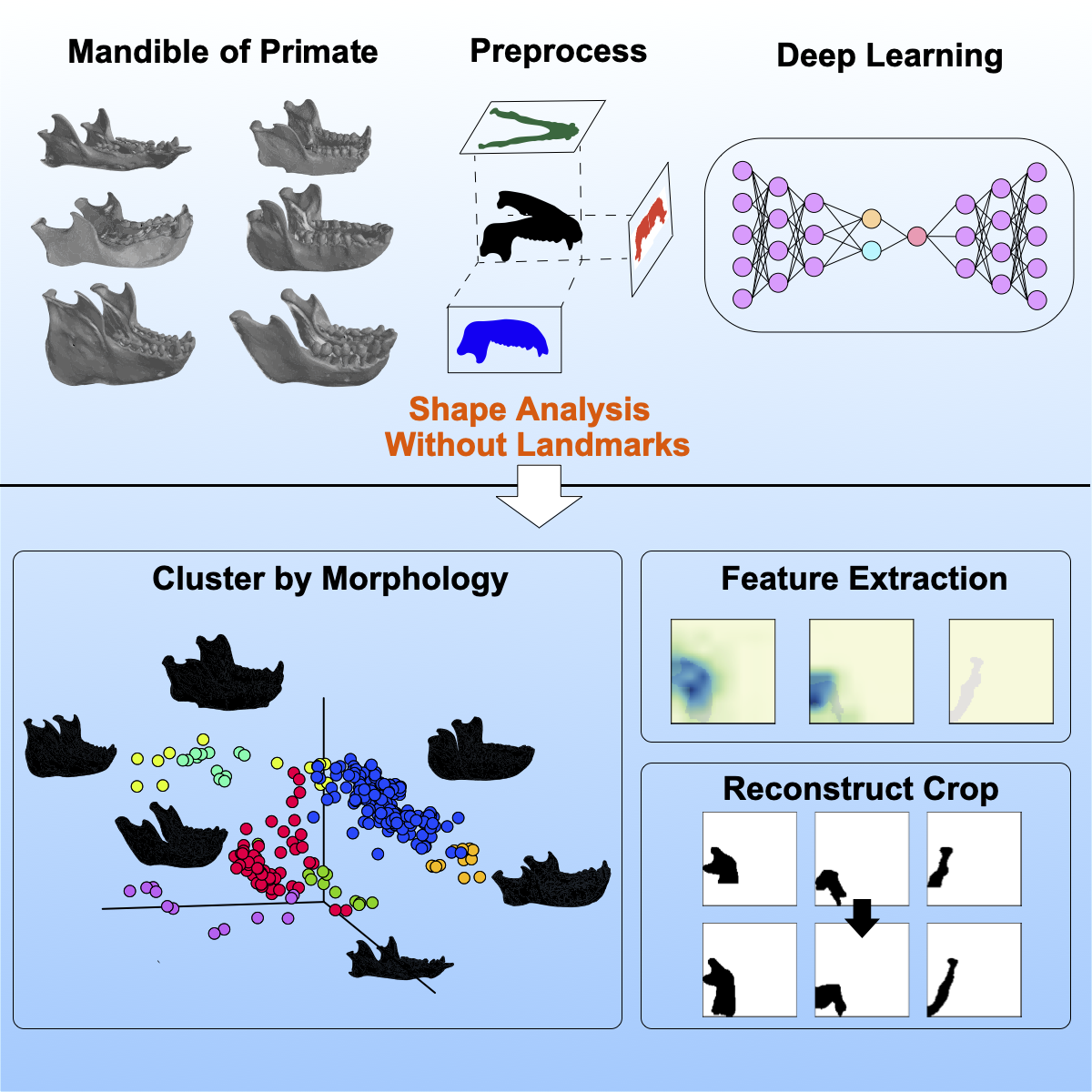
Overview
Morphology is a phenotype acquired over a long period of time. There are as many morphologies as there are organisms in the world, and even the same organism has slightly different morphologies. Morpho-VAE is an innovative model that represents these differences using deep learning.
Key Features
- Landmark-free: Unlike conventional methods, no specific point designation is required
- Robust to missing data: Analysis possible even with incomplete data
- Application to mandible shape: Effectiveness demonstrated in primate mandible morphology analysis
Technical Details
Using a deep learning architecture based on Variational Autoencoder (VAE), high-dimensional morphological data is efficiently mapped to low-dimensional latent space. Successfully extracts features that distinguish species/families.
Applications
Wide-ranging applications expected in evolutionary biology, morphology, medical image analysis, archaeology, and other fields.
Related Links:
🔬 KANADE: Batch Effect Removal Technology
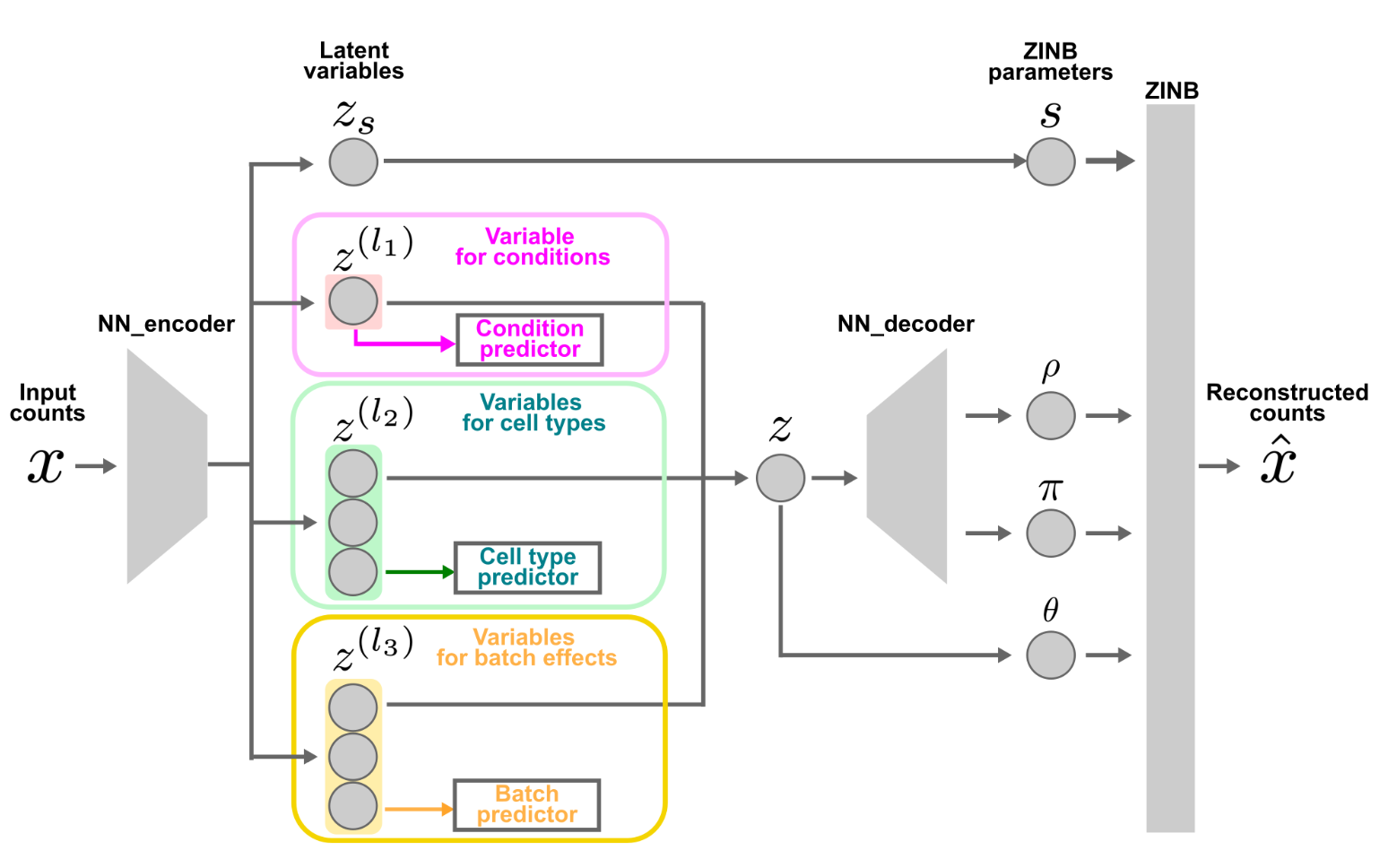
Background
In single-cell transcriptomics, batch effects due to differences in experimental conditions are a major obstacle to analysis. Conventional methods have the problem of simultaneously removing biological signals.
KANADE’s Innovation
KANADE is a new method that cleverly distinguishes between biological signals and batch effects by applying Morpho-VAE. Using deep learning, it removes only technical variation while preserving the essential biological patterns in the data.
Key Features
- Variational Autoencoder: Efficient representation learning through deep learning
- Selective batch effect removal: Preserves biological signals, removes only technical variation
- Scalability: Handles large-scale datasets
- Versatility: Applicable to various single-cell analyses
Practicality
Demonstrates power in integrative analysis, meta-analysis, and database construction from multiple experimental batches.
Related Links:
🧠 Mathematical Model of Social Stress
Research Objective
Aims to quantitatively analyze the effects of social stress on individual behavior and physiology using mathematical models and clarify the basic principles of stress response.
Approach Methods
- Energy landscape analysis: Physically represents transitions in psychological states
- Bayesian inference: Probabilistic modeling of ruminative thinking in the brain
- Free energy principle: Analysis based on unified theory of cognitive processes
- DOLO (Drosophila tracking with YOLO): Automated behavior tracking using deep learning
Research Achievements
Achieves results through multi-layered approaches including psychological state changes during emergency declarations, mouse behavior under social defeat stress, and Drosophila larva behavior analysis.
Future Prospects
Aims to contribute to understanding and treatment development of stress-related disorders through applications in psychiatry, behavioral science, and social science.
Related Links: